Odit-e is a French company founded in 2017 offering artificial intelligence (AI) solutions to support planning, management and maintenance of low-voltage (LV) electricity and drinking water distribution networks. Based in Meylan, near Grenoble, the company became a subsidiary of Sagemcom in 2023. In 2021, it won the Digital Energy Challenge for a project to digitize the LV electricity network in partnership with TANESCO, the Tanzanian public electricity company, paving the way for smart metering in Tanzania. Thanks to the AI module developed by Odit-e, TANESCO will be able to exploit data from smart meters located on the low-voltage network in Moshi, in the north-east of the country. The Odit-e tool, which can be used to analyze the state of the low-voltage network (load and voltage levels in particular), as well as to locate and quantify non-technical losses, is intended for deployment in other low-voltage zones operated by TANESCO.
You can find out more about this project on our website here.
What are the different areas of application for data from smart meters on low-voltage networks?
Arthur Forestier: Analyzing data from smart meters enables us to provide distribution system operators (DSOs) with solutions for a variety of use cases. The algorithms developed by Odit-e offer five types of service, based on a digital twin that mimics the electrical behavior of the LV network:
Topology: to complete or correct asset databases (GIS in particular), Odit-e tracks the associations of meters with their MV/LV substation, the feeder feeding them, and the phase(s) to which they are connected to the network. In this way, Odit-e saves the DSO a great deal of fieldwork, which can be quite extensive.
Network analysis: Network constraints are assessed, such as the load level of MV/LV substations and the voltage plan of the LV network. The aim is to provide DSOs with an overall view of network constraints, in order to optimize maintenance and investment.
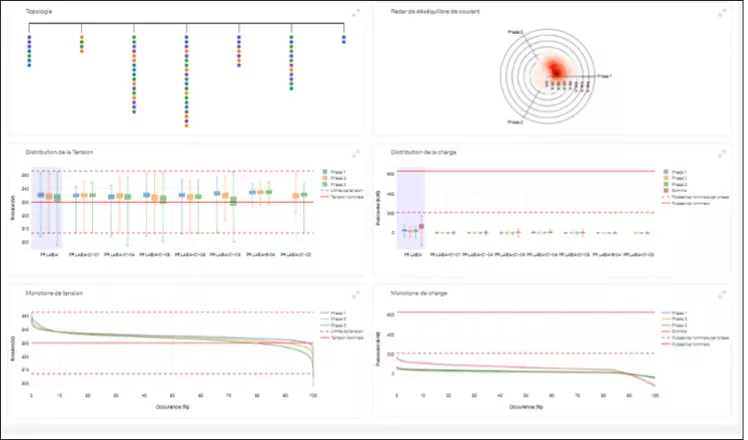
Figure 1 - Network analysis tool
Phase balancing on the network: Load imbalances between the different phases of a network cause premature wear and tear on equipment, and make it difficult to connect new assets. To alleviate these problems, Odit-e's solution offers a balancing plan that suggests swapping the phases of certain meters (see the “With” line below) to improve imbalance levels and consequently reduce constraints.
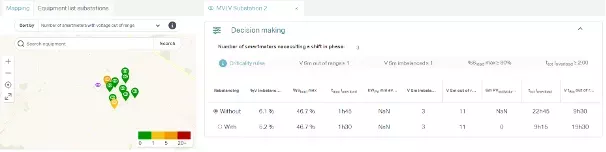
Figure 2 - Grid rebalancing tool
Photovoltaic capacity: Based on the network constraints identified elsewhere, we estimate for each communicating meter the photovoltaic production capacity it can accommodate without degrading network indicators (voltage levels, transformer load, etc.). The customer can view this information in the form of a map or table.
Soon, we will be providing a similar tool to assist DSOs with the connection of electric vehicle charging stations and heat pumps.
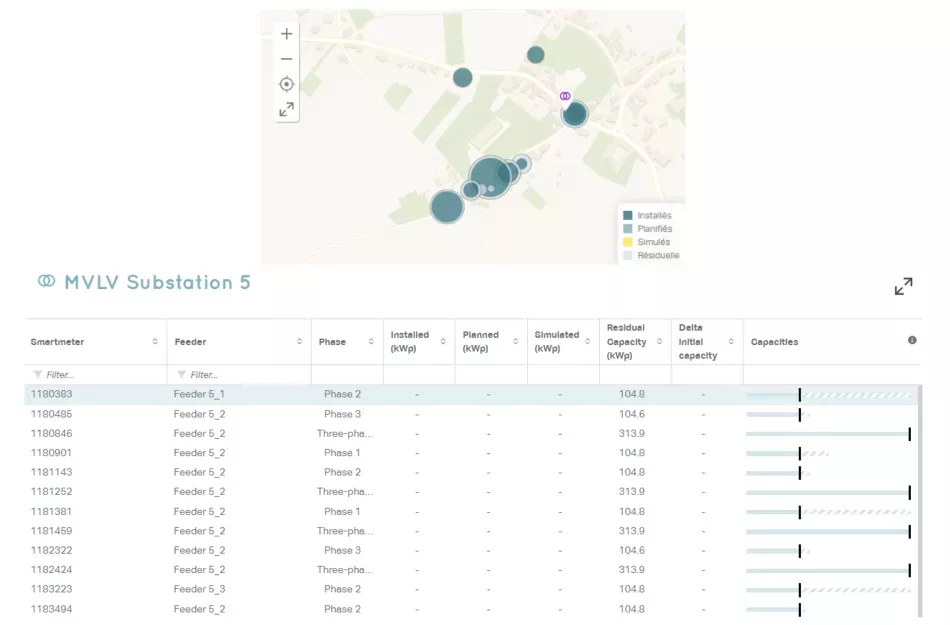
Figure 3 - Photovoltaic mapping tool
Detecting non-technical losses: This is the focus of our project in Tanzania. Odit-e deploys smart meters to cover a pilot area and cross-references aggregated consumption data with transformer station data to deduce the volume of non-technical losses. Localized detection of losses is achieved by measuring any voltage drops between meters in the same geographical area. This eliminates the need for field research, which is sometimes laborious for DSOs due to the diffuse nature of distribution networks.
What technological developments are underway in this field, and what opportunities does this represent for Odit-e?
Luc Richaud: Against a backdrop of increasing renewable production capacity and the emergence of new electrical uses, the development of flexibility management solutions for the low-voltage grid is an emerging market. Current research projects, particularly in Europe, aim to control flexibilities in real time, such as heat pumps and charging stations for electric vehicles. In particular, Odit-e has taken part in the GIFT research project, which deals with local flexibility markets for island networks connected to the mainland by a single cable.
In addition to technological developments, we should also mention the main challenges facing the use of data from DSO information systems (smart meters, GIS, SCADA, etc.). One of the main challenges is the availability of data, the quantity and quality of which determine the accuracy of the results provided by the models. Many metering infrastructures have been designed primarily to enable remote billing of customers, and do not necessarily provide the information required by our algorithms and analysis methods. Furthermore, the data models provided by meters vary from country to country and from DSO to DSO. Algorithms must therefore be robust and adaptive to these changes.
What is your perception of markets on the African continent? Do you plan to expand there?
Arthur Forestier: The solutions offered by Odit-e are based primarily on the implementation of smart meters in the countries concerned, and therefore on their Smart Metering strategies. The acquisition by Sagemcom means that we now have an integrated offering (meters + HES/MDMS software + data analysis). However, this is a competitive market, with relatively low prices and strong competition on the hardware side. Calls for tender do not always include a request for an analysis service in addition to this hardware component, even though this could improve the ROI of the operation for the DSO by seeking other ways of increasing the value of the metering infrastructure.
In this respect, the project with TANESCO is a great success, and a fine demonstration of the added value of using smart meter data. We hope to extend our activities to other African countries.
In one sentence, what's the latest news from your company?
Luc Richaud: Odit-e is currently carrying out its first large-scale deployment of its topology and balancing solutions.



